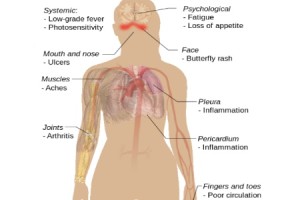
Wide spread Lupus Erythematosus Manifestations – Systemic lupus symptoms
SLE influences multiple organ devices. The Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Manifestationsadvancement is visible by remissions and regressions and could vary from moderate to intense.
Mucocutaneous – A lot of people have skin lesions at some time during the advancement of the condition. Butterfly breakout, erythema or redness over the cheeks and nose, saving the nasolabial layers, which shows up after sunlight exposure is the most usual lesion. It usually persists however lasts a few days. Some people will certainly get discoid sores, that are more inflammatory and have a scarring propensity. Alopecia or baldness is common, yet thinning hair is unheard of.
Arthritis – Joint Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Manifestationswhich are often the earliest indication take place in over 90 % of people at time throughout the health problem. Just a few joints are typically had an effect on, specifically those of the hands. The SLE arthritis has the tendency to be strolling and in proportion. The arthritis is relatively uncomfortable, and hardly ever warping.
12 to 45 percent of clients have dental and/or nasal ulcers, usually pain-free, unlike herpetic chancre scorchings.
Raynaud sensation – Happened in 16 to 40 % of clients, Chilly or emotion-induced color changes of the figures of the hands and/or feet, the Raynaud phenomenon, is a frequent trouble and might antedate various other attributes of the ailment.
Gastrointestinal tract – Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Symptom is usually included GI tract, but more often from medicine negative effects than from energetic SLE. Instances of the previous consist of gastritis and even peptic ulcers secondary to using NSAIDs alone or in combo with glucocorticoids. SLE vasculitis can bring about pancreatitis, peritonitis, and colitis. Signs of esophageal irritation or reflux could develop. Nonspecific stomach discomfort is regular.
Renal – Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Symptoms of Kidney ended up being clinically obvious in roughly 50 percent of clients; however, most of the continuing to be clients have subclinical ailment that could be demonstrated if renal biopsy were executed. Renal participation normally develops in the first few years of health problem, and should be identified early by routine urinalyses, quantitation of proteinuria, and estimation of the glomerular filtering price (normally by overseeing the plasma creatinine concentration). A number of kinds of glomerulonephritis can take place and renal biopsy serves to determine the type and level of renal involvement.
Cardiovascular – There are a selection of cardio signs of SLE. Pericarditis is rather usual, while verrucous (Libman-Sacks) endocarditis is normally medically quiet however can generate valvular lack and function as a resource of emboli (image 5). Patients with SLE have an enhanced threat of coronary artery condition.
Lung – Pleurisy, pleural effusion, pneumonitis, interstitial lung condition, pulmonary hypertension, and alveolar hemorrhage can all happen in SLE. The threat of thromboembolic involvement is boosted in those with antiphospholipid antibodies. Dyspnea, episodic pleuritic breast pain, dynamic decrease in lung amount in the absence of interstitial fibrosis or substantial pleural ailment recommends the shrinking lung disorder. Pulmonary feature tests are often substantially unusual, with limiting irregularities, before complaints of dyspnea.
Neurologic – Neurologic complications include cognitive defects, organic brain syndromes, delirium, psychosis, seizures, headache, and/or peripheral neuropathies. Other less common problems are movement disorders, cranial neuropathies, myelitis, and meningitis.
Psychosis, which may be due to SLE or to glucocorticoid treatment, is one of several psychiatric manifestations of SLE. Others include: depression, anxiety, and mania.
Neonatal lupus can cause heart block of varying degrees that may be noted in utero and or present as congenital heart block.
Thromboembolic events, often in association with antiphospholipid antibodies, may occur in a substantial minority (20 percent) of patients with SLE. Arterial thromboemboli may cause focal neurologic problems, such as stroke or seizures, and/or more diffuse cognitive defects
Ophthalmologic – The eye is frequently involved in SLE with the most common manifestation being keratoconjunctivitis sicca. rare ophthalmologic manifestations of SLE include: Cotton wool exudates due to retinal vasculitis, Anterior uveitis, Episcleritis or scleritis.
Hematologic– Cytopenias and thrombophilia, an increased the propensity to develop thromboembolic disease, might be features of SLE. Leukopenia which is diagnostically useful is common. While, it is usually not symptomatic unless severe (less than 2000/mm3). 43 to 66 % of patients have leukocyte count of less than 4500/mm3. Many patients have a mild anemia, which is most often due to the anemia of chronic disease.
Lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly – Many patients have peripheral lymphadenopathy and/or splenomegaly.
Anticardiolipin antibodies can produce a false positive test for syphilis (eg, VDRL).
Immunologic – Autoantibody production is a hallmark of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Symptoms.